Why Waterproof Breathable Membranes with the Same Specs Perform Very Differently: The Hidden Science of Precision
In the global procurement of functional textiles and protective materials, buyers often encounter a perplexing paradox: two waterproof breathable membranes from different suppliers may present identical values on a Technical Data Sheet (TDS)—the same Hydrostatic Head and the same Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR). Yet, when these materials are converted into final products, such as surgical gowns or diaper backsheets, their real-world performance diverges dramatically. The root of this discrepancy lies in the "invisible variables" that standard specification sheets fail to capture: microscopic pore uniformity and lamination integrity. This article delves into the advanced material science behind Kae Hwa Industrial’s Casting Film Technology and In-Line Lamination process, revealing how a precision tolerance of 0.01 mm creates the difference between a product that passes a lab test and one that protects a life.
Why Do Membranes with the Same Specs Perform Differently?
When you compare Technical Data Sheets (TDS) from two different suppliers, and both state a Hydrostatic Head > 10,000 mmH2O and MVTR > 3,000 g/m²/24hr, it is natural to assume these materials are equivalent.
For general applications, this assumption might hold. However, for critical sectors requiring extreme safety—such as medical protection (ASTM F1671), industrial safety (Type 4B/5B/6B), or high-performance outdoor gear—relying solely on average data points is a risk.
A specification sheet typically represents "static average values" derived from controlled laboratory conditions. It fails to answer three critical questions regarding real-world reliability:
- Consistency: Is the thickness consistent from the first meter of the roll to the 5,000th meter?
- Micro-Structure: Are the microscopic pores distributed evenly, or are there localized defects that could lead to leakage?
- Lamination Bond: Will the membrane separate (delaminate) from the fabric after washing, abrasion, or sterilization?
At Kae Hwa Industrial, with over 60 years of expertise in chemical engineering, we know that true protection is built on the extreme control of microscopic structures.
The Blind Spot of Data: The "Micro-Truth" Not Shown on Spec Sheets
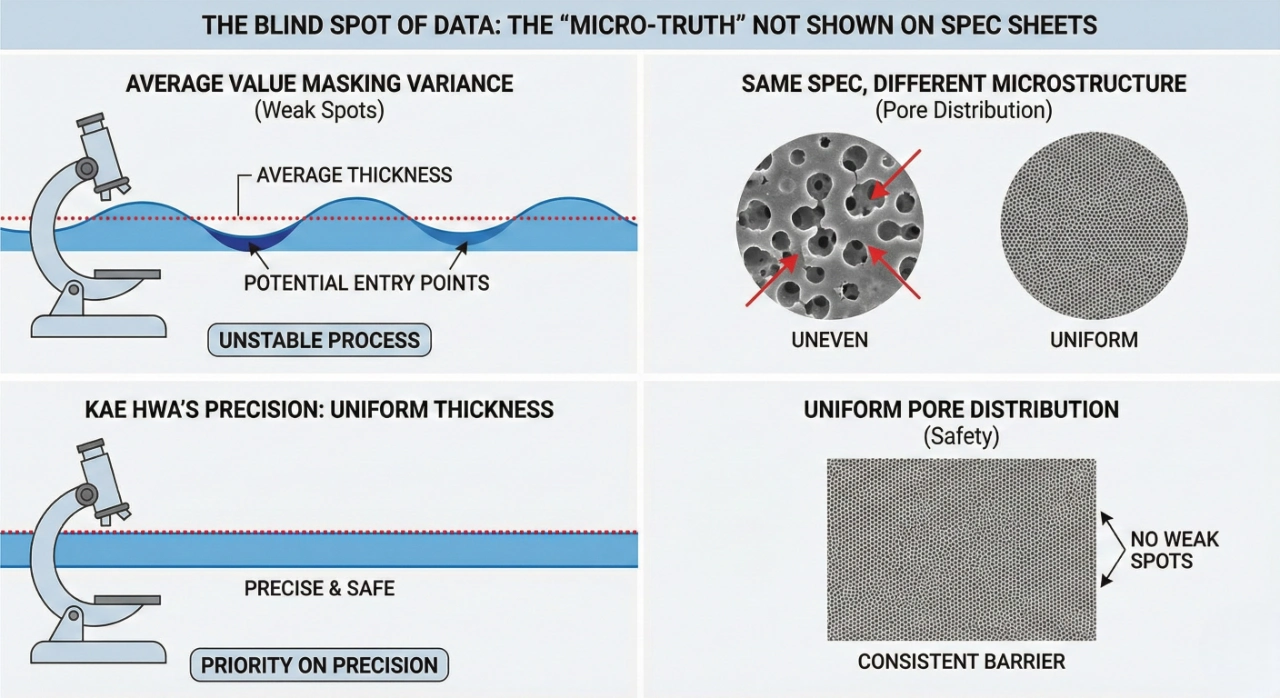
In material science, "average values" often mask "variance." If a membrane's production process is unstable, its thickness may fluctuate. While the average thickness meets the specification, the thinner areas (weak spots) become potential entry points for viruses or liquids under pressure.
This is why Kae Hwa prioritizes precision over simple compliance. We believe that a deviation of even 0.01 mm is not just a statistical error—it is a potential safety breach for a surgeon or an industrial worker.
The Precision of Casting Film Technology
The first determinant of membrane quality is the manufacturing process itself. Kae Hwa utilizes advanced Casting Film Technology, which serves as the foundation of our quality consistency.
Thickness Tolerance Control: ± 0.01 mm
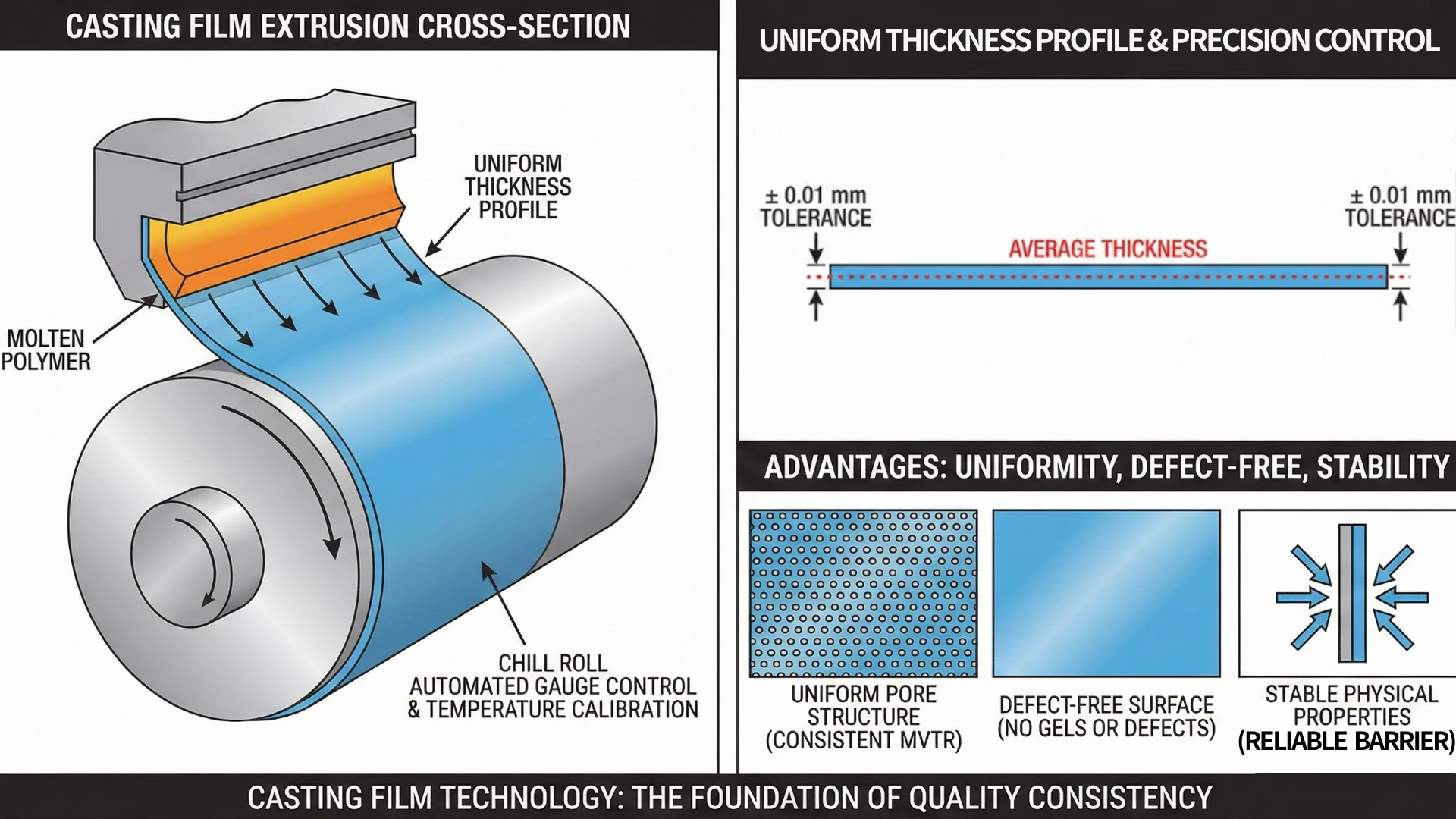
By utilizing precision dies to extrude molten polymer, coupled with automated gauge controls and temperature calibration, we strictly maintain a film thickness tolerance within ± 0.01 mm. This extreme precision delivers three distinct advantages:
- Uniform Pore Structure: This ensures that the Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR) is consistent across every inch of the fabric. Users will not experience "hot spots" where breathability is blocked or "leak spots" where pores are too large.
- Defect-Free Surface: The casting process creates an exceptionally smooth surface free from "gels" or crystalline defects. This is crucial for hygiene applications (like diaper backsheets) where tactile softness and visual purity are paramount.
- Stable Physical Properties: Whether it is our MicroBreath™ microporous series or AquaVene™ monolithic series, the uniform structure ensures reliable barrier performance in diverse environments.
In contrast, films produced with less precise methods may suffer from uneven cooling and crystallization, leading to inconsistent pore distribution—the primary reason why a material might "pass the lab test" but fail in the field.
In-Line Lamination Determines Product Longevity
A membrane is rarely used in isolation; it is usually laminated to a nonwoven or woven fabric. This lamination stage is often where performance degradation occurs. Many quality issues, such as delamination or reduced breathability, stem from traditional "off-line" lamination processes.
Kae Hwa employs a sophisticated In-Line Lamination Technology, which resolves the fundamental flaws of traditional bonding:
1. No Reheating Required (Preserving Structural Integrity)
Our process bonds the film to the substrate immediately after extrusion, utilizing the film's residual thermal energy.
- The Advantage: This eliminates the need for "rewinding" and "reheating" steps found in off-line processes. Secondary heating can damage the delicate microporous structure, causing pores to collapse (lowering breathability) or melt (lowering waterproofing). Kae Hwa’s one-step process preserves the membrane’s original engineered performance.
2. Solvent-Free Manufacturing (Eco-Friendly & Safe)
Our In-Line Lamination is a completely Solvent-Free process.
- The Advantage: We eliminate the use of chemical adhesives that release Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). This ensures a cleaner production environment and results in a safer final product with no chemical residues—essential for MediShield™ medical gowns and HygieSoft™ baby hygiene products that contact skin directly.
3. Molecular-Level Bonding
Bonding the materials while they are in a compatible thermal state creates superior adhesion strength. Our composite fabrics resist delamination even after repeated washing, physical stretching, or sterilization, significantly extending the product's lifecycle.
Lab Data vs. Real-World Stability
The true test of a material is not in a climate-controlled laboratory, but on a stormy mountain peak, in a chemical plant, or inside an isolation ward. Kae Hwa’s materials are trusted in over 100 countries because they are validated against the most rigorous international standards for real-world scenarios:
- Medical Viral Protection: Our MediShield™ series passes the ASTM F1671 viral penetration test, confirming its ability to block blood-borne pathogens and bacteriophages. It meets AAMI Level 4 standards, the highest level of protection for surgical gowns.
- Industrial Chemical Barrier: Our InduBarrier™ series is certified for CE Type 4B / 5B / 6B, proving its resistance to liquid chemical sprays, hazardous particles, and infective agents.
- Extreme Weather Resistance: For construction (BuildBreathe™) and outdoor (ProShell™) applications, our materials undergo specialized UV stability and aging tests to ensure they perform consistently despite long-term exposure to sun and temperature fluctuations.
These certifications are not just documents; they are the validation of our "0.01 mm precision" promise.
Choose the "Invisible Precision"
In the world of waterproof breathable materials, the specifications are what you see, but the manufacturing process is what you trust. It is this "Invisible Precision"—from the ± 0.01 mm control of Casting Film Technology to the integrity of Solvent-Free In-Line Lamination—that defines the true value of the product.
Do not let a generic data sheet dictate the safety of your end-users. By choosing Kae Hwa Industrial, you are choosing not just high-quality PE/PP/TPEE films, but 60 years of material science expertise dedicated to your success.
👉 Contact Kae Hwa for a precision evaluation tailored to your application.
FAQ
Q1: Why do some breathable membranes lose performance or feel "damp" after prolonged use?
A: This is often due to the collapse or clogging of the microporous structure. If the film manufacturing is unstable, pores can deform under pressure. Kae Hwa’s MicroBreath™ series utilizes a rigid, uniform pore structure formed by precision casting, and our In-Line Lamination prevents adhesive from blocking these pores, ensuring long-lasting breathability.
Q2: How should I choose between Microporous and Monolithic (Hydrophilic) films?
A:
- Microporous (e.g., MicroBreath™): Best for applications requiring high airflow and vapor transmission, such as diaper backsheets, protective coveralls, and roof underlays.
- Monolithic (e.g., AquaVene™): Best for applications requiring extreme waterproofness, viral barriers (ASTM F1671), and chemical resistance. It relies on molecular diffusion, making it solid, durable, and impenetrable to viruses. Kae Hwa manufactures both and can advise the best solution for your specific need.
Q3: Can In-Line Laminated products be customized?
A: Absolutely. Our In-Line Lamination system is highly flexible. We can laminate our films to various substrates (Spunbond, Meltblown, Woven fabrics) and even integrate 4-Color Printing directly onto the film during the process. This allows for branding or pattern designs without compromising the membrane’s breathability or waterproof integrity.
.webp)