How TPEE Differs from General TPE in Functional Textile Applications
How molecular structure dictates performance
Among advanced thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), TPEE (Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer) stands out for combining the strength and heat resistance of engineering plastics with the flexibility of rubber. Its unique block-copolymer architecture delivers stable elasticity, excellent fatigue life, and high durability—properties that distinguish it from conventional TPE materials used in footwear, automotive, or textile applications.
While TPE is an umbrella term for multiple chemistries—including polyolefin-based (TPO), styrenic (TPS), dynamically vulcanized (TPV), polyurethane (TPU), and the polyester-based (TPEE) systems—TPEE’s composition is key. Its polyester segments deliver high crystallinity and a stable morphology that make its performance notably different from general TPE grades.
Molecular structure differences between TPEE and General TPE
TPEE: a two-phase block copolymer
TPEE is a block copolymer composed of alternating segments with distinct roles:
- Polyester hard segments form microcrystalline domains that provide strength, stiffness, and thermal stability.
- Polyether soft segments create amorphous, flexible regions that deliver high elasticity and low-temperature toughness.
This “hard-and-soft” architecture enables TPEE to maintain stable mechanical properties under tensile load, repeated flexing, and wide temperature swings.
General TPE: typically a single polymer system
General TPE compositions vary by subtype. Common TPO or TPS materials are polyolefin- or styrenic-based. They’re soft and easy to process, but the lack of robust crystalline hard domains limits heat resistance and fatigue life.
As a result, TPE suits shorter-life or lower-load uses, while TPEE handles prolonged stress, repeated deformation, and more extreme environments.
TPEE vs. General TPE Core Performance Comparison
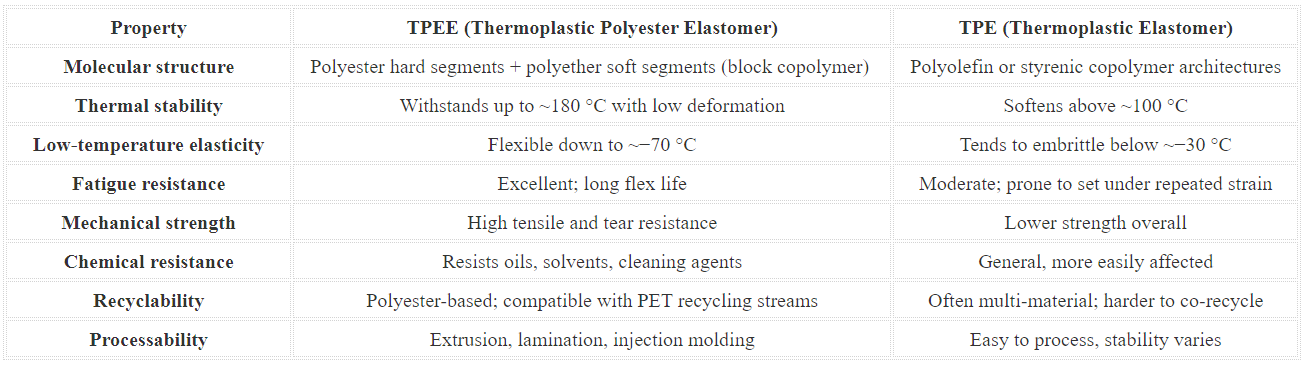
The crystalline hard segments in TPEE deliver strength and long-term stability, while the soft segments preserve elasticity. TPEE outperforms general TPE in heat resistance, chemical resistance, and fatigue life. In applications that demand durability and reliability (e.g., protective fabrics or industrial films), TPEE significantly improves service life and performance consistency.
TPEE in waterproof-breathable technology
Monolithic, pore-free moisture transport
Conventional microporous films rely on pore size to pass water vapor while blocking liquid water. Pores can clog with skin oils, detergents, or dust.
TPEE films (monolithic films) use a pore-free, hydrophilic mechanism that transports water vapor via molecular diffusion, achieving waterproof and breathable performance without pores.
Core attributes:
- MVTR (moisture vapor transmission rate): 10,000–20,000 g/m²·24 h
- Hydrostatic head (EN 20811): ≥10,000 mmH₂O
- Stability: Performance is not degraded by oils or detergents, retaining function over time.
This construction is well suited for medical protective apparel, outdoor waterproof-breathable jackets, and other garments worn for extended periods.
Strong heat and chemical resistance
The polyester backbone of TPEE enables sustained thermal stability and resistance to chemical agents. Even after repeated wash cycles, tumble drying, or exposure to high-temperature disinfection, TPEE maintains its elasticity and strength. Typical uses include:
- Medical protective and isolation fabrics
- Industrial fabrics requiring oil, solvent, and dust resistance
- Heat-resistant hoses, gaskets, and structural films
Stable processing and lamination flexibility
TPEE can be processed via extrusion, blown film, thermal pressing, or PUR hot-melt lamination.
Its robust mechanical profile tolerates thermal lamination, sewing, and post-processing such as printing.
TPEE also laminates directly to polyester textiles (PET or rPET), enabling mono-material lamination that simplifies end-of-life recycling and reprocessing.
Where TPEE excels
.webp)
Functional apparel and outdoor gear
In outdoor and athletic garments, TPEE provides stable waterproof-breathable performance along with low-temperature flexibility and fast elastic recovery.
The soft hand feel and long-term durability help laminated garments retain performance after repeated folding and washing.
Medical and protective applications
TPEE’s chemical resistance and barrier properties make it a reliable choice for medical protective wear and surgical textiles.
It can meet ASTM F1671 viral penetration resistance and EN 14126 infectious barrier performance while maintaining comfort through breathability.
Industrial and structural applications
For industrial use, TPEE serves as a material for conveyor belts, hydraulic hose components, sealing films, and composite fabric layers.
Its creep resistance and abrasion resistance suit higher pressure, higher temperature, or continuous-duty environments.
Polyester architecture and circularity
Because TPEE is polyester-based, it pairs naturally with polyester fabrics in mono-material constructions that are easier to recycle.
Compared with PU or some TPU systems, TPEE can be more readily regenerated in chemical recycling pathways and can reduce reliance on solvent-borne adhesives.
This makes TPEE a strong fit for sustainability-driven textile designs, especially as mono-material strategies gain adoption.
Explore the Advantages of TPEE for Functional Textiles
Discover how Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer (TPEE) enhances the performance and comfort of modern functional fabrics.
Key benefits of TPEE:
High mechanical strength with lasting elasticity
Stable performance across a wide temperature range
Excellent chemical resistance with waterproof-breathable balance
Polyester-based recyclability for sustainable, mono-material design
Ideal for outdoor apparel, sportswear, and medical or protective garments, TPEE films deliver reliable comfort, durability, and circular-design potential.
FAQ
Q1: What’s the primary difference between TPEE and general TPE?
TPEE is a polyester-based block copolymer that combines high elasticity with strength. Most general TPE grades are polyolefin-based and softer but less stable over time.
Q2: How heat-resistant is TPEE?
TPEE can operate up to roughly 180 °C and remains flexible at low temperatures down to about −70 °C, making it suitable for environments with large thermal swings.
Q3: How can TPEE be both waterproof and breathable?
TPEE films use a pore-free, hydrophilic mechanism. Water vapor diffuses through the polymer matrix while liquid water is blocked, so breathability and water resistance coexist.
Q4: Is TPEE recyclable?
Yes. Being polyester-based, TPEE can be paired with polyester fabrics in mono-material laminations that fit PET recycling streams.
Q5: Where is TPEE film commonly used?
In medical protective fabrics, outdoor waterproof jackets, industrial protective wear, footwear components, and high-durability laminated fabrics.
.webp)