Industrial Protective Fabrics: Type 5/6 Chemical & Dust Barrier
.webp)
Industrial safety managers face a dual challenge: protecting workers from hazardous chemicals and dust while preventing heat stress. This guide analyzes Kae Hwa's InduBarrier™ Series, a microporous laminated fabric engineered for the industrial sector. We explore its compliance with Type 4B/5B/6B standards, its superior Antistatic (EN 1149-5) properties for explosive environments, and its added value of EN 14126 biohazard protection for waste management sectors.
Engineered for Industry: Advanced Microporous Fabrics for Chemical and Dust Protection
The Industrial Challenge: Balancing Barrier and Breathability
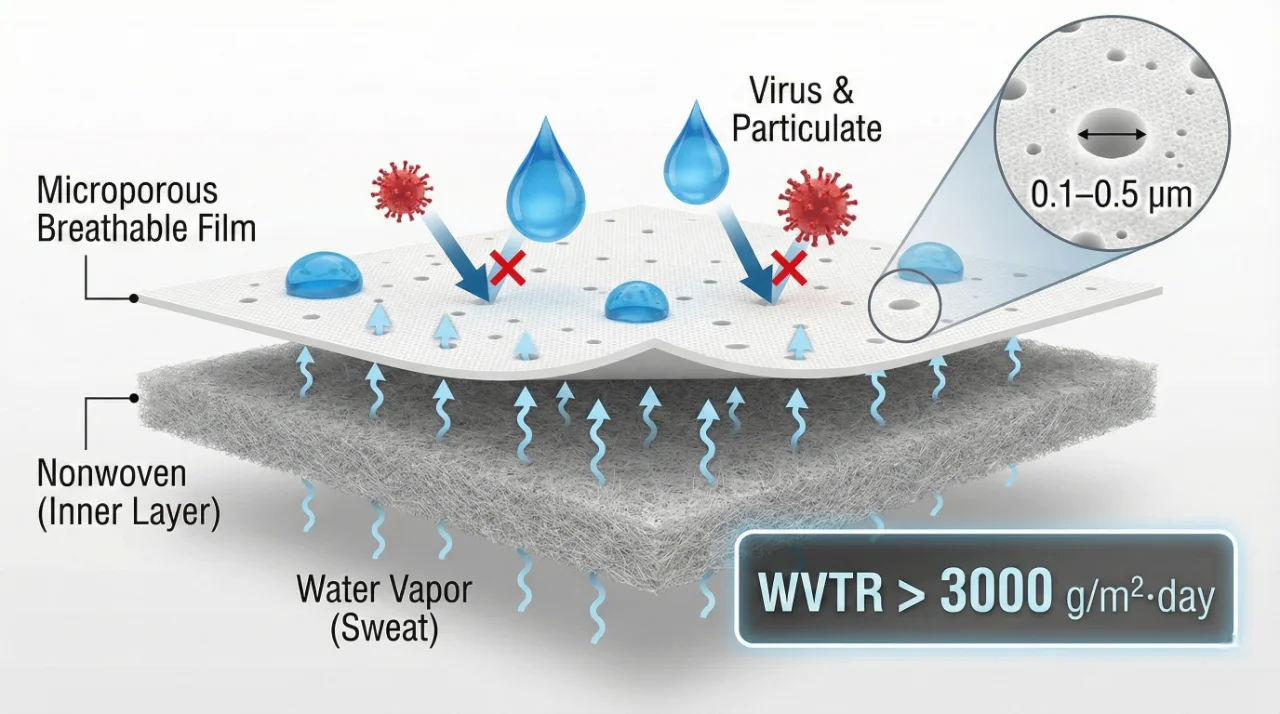
In heavy industry—from automotive painting to petrochemical maintenance—workers are often encased in protective suits for hours. The primary risks are obvious: hazardous dust (asbestos, silica) and chemical splashes. However, the secondary risk is silent: Heat Stress .
Traditional PVC or solid PE coated fabrics act like plastic bags, trapping body heat and causing fatigue. The modern industrial standard has shifted to Microporous Laminated Technology .
The InduBarrier™ Solution:
By laminating a microporous breathable film to a durable nonwoven, we create a specialized "selective barrier":
- Blocks: Liquid chemicals, oils, and pressurized dust.
- Releases: Sweat vapor (High MVTR), keeping the worker dry and focused.
Core Industrial Standards: Type 4/5/6 & Antistatic
For industrial procurement, "Standard Compliance" is the baseline for safety. Our fabric is engineered to meet the stringent requirements of Category III PPE :
Particle & Splash Protection (The Primary Defense)
- Type 5 (EN 13982-1): Proven defense against hazardous dry particles (e.g., asbestos, fiberglass). The fabric's structure prevents microscopic dust from penetrating the weave.
- Type 6 (EN 13034): Resistance to light mist and liquid chemical splashes.
- Type 4 (EN 14605): With specific taping, the material passes spray saturation tests, offering a higher tier of liquid defense.
The Critical Importance of Antistatic (EN 1149-5)
In volatile environments like paint shops or refineries, a static spark can be catastrophic.
Safety Feature: InduBarrier™ fabrics are treated with a conductive coating on both sides, ensuring a surface resistance of <2.5 x 10⁹ Ω. This prevents electrostatic buildup, protecting against explosion risks and reducing dust attraction.
Chemical Repellency & Physical Durability
Industrial gear gets beaten up. It must withstand abrasion while repelling aggressive fluids.
Chemical Repellency (EN 368)
It’s not just about blocking water; it’s about repelling acids and bases. The InduBarrier™ fabric demonstrates a Class 3 Repellency Index (the highest material rating) against common industrial hazards:
- 30% Sulphuric Acid
- 10% Sodium Hydroxide
- o-Xylene & Butan-1-ol
Rugged Durability
Unlike medical gowns, industrial suits face rough surfaces.
- Abrasion Resistance (EN 530): Class 1 compliance ensures the film doesn't rub off easily.
- Flex Cracking (ISO 7854-B): Withstands >5,000 cycles, ensuring the barrier stays intact even when workers are bending, crawling, or reaching.
The "Dual-Use" Advantage: Biological Protection (EN 14126)
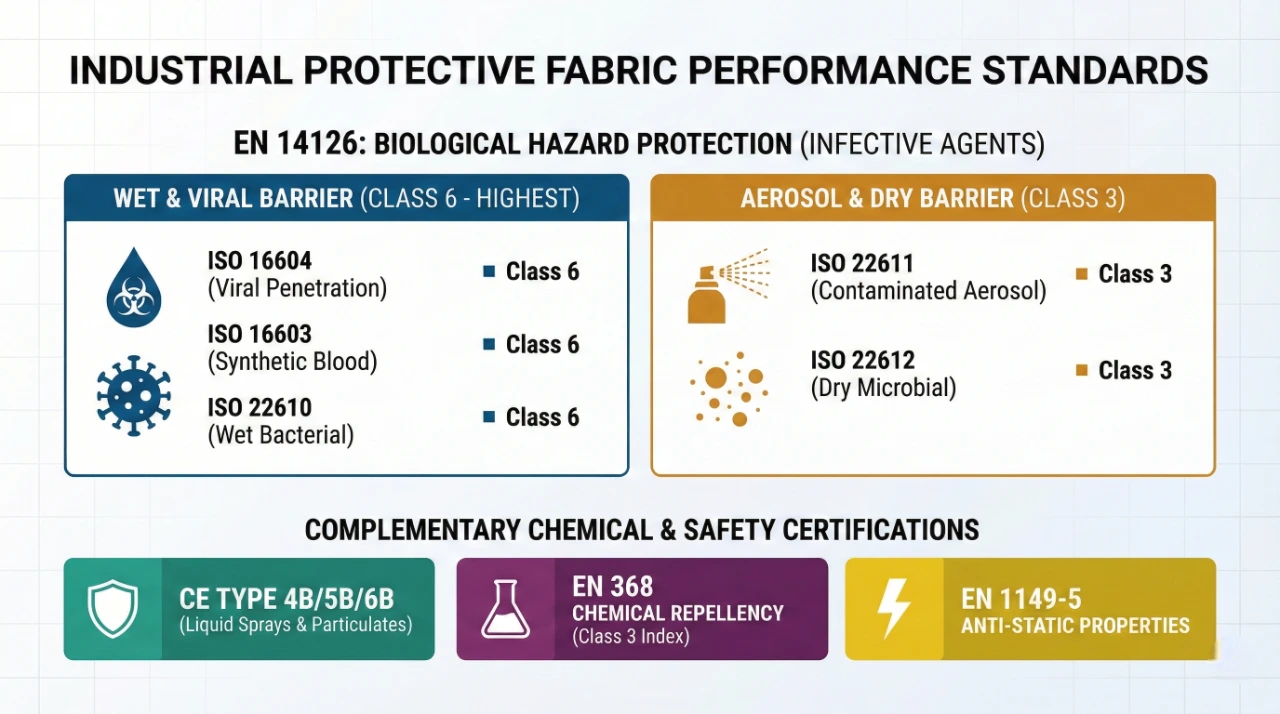
While primarily an industrial fabric, InduBarrier™ offers a unique "Dual-Protection" value.
For sectors like Waste Management, Sewage Maintenance, or Agriculture, workers face mixed risks: chemicals and pathogens.
- EN 14126 Certified: The fabric achieves the maximum Class 6 rating for viral penetration (ISO 16604).
- The Benefit: This allows one inventory item (the InduBarrier™ suit) to serve multiple departments—from the chemical mixing room to the wastewater treatment plant—simplifying PPE procurement.
Customization for PPE Manufacturers
Kae Hwa leverages 60 years of expertise to support OEM partners. We don't just sell rolls; we tailor the spec:
- Weight: From ultra-light 43 gsm (for painting) to heavy-duty 83 gsm (for construction).
- Identification: Available in Industrial White, Safety Orange, Blue, or Yellow.
- Dimensions: Custom slit widths (1524mm - 1550mm) to optimize your cutting table efficiency.
👉 Equip your workforce with the best. Contact Kae Hwa for InduBarrier™ swatches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is Microporous fabric better than SMS for industrial use?A: While SMS is breathable, it is porous and can allow liquid pressure to penetrate. Microporous Laminates offer a superior liquid barrier (Hydrostatic Head) and better chemical repellency, making them safer for wet industrial tasks while maintaining breathability.
Q2: Is this fabric suitable for explosive atmospheres?A: Yes, provided the garment is properly grounded. The fabric meets EN 1149-5 (Antistatic) standards, which is designed to prevent incendiary discharges in zones with flammable gases or dust.
Q3: Can I use this fabric for both chemical and sewage work?A: Yes. This is the InduBarrier™ advantage. Because it passes both EN 368 (Chemical Repellency) and EN 14126 (Biohazard), it is a versatile solution for diverse hazardous environments.