Desiccant Packaging Materials — Breathable Film Solutions for Moisture Control
.webp)
In tropical and subtropical regions, humidity is not just a seasonal factor—it’s a constant environmental challenge. For everyday moisture-sensitive items such as deodorant packs and hand warmers, persistent exposure to humid air can accelerate degradation or cause inconsistent performance. Kae Hwa’s desiccant packaging materials, engineered with breathable laminated films, regulate vapor transmission to balance moisture control and air circulation—keeping products stable even under long-term humidity stress.
Desiccant Packaging Materials with Breathable Films for Deodorant and Hand Warmer Applications
Why Breathable Films Matter in Desiccant Packaging
Conventional plastic packaging may provide a perfect moisture seal, but for desiccant-based or oxidation-driven products, that very barrier becomes a limitation. When air cannot circulate or vapor cannot escape, the active material inside either saturates prematurely or fails to react at a stable rate.
In deodorant sachets, sealed films can trap moisture within the pack, causing clumping and reducing adsorption efficiency. In hand warmers, over-restricted airflow slows the oxidation process that generates heat, leading to inconsistent or weaker performance.
Breathable laminated films solve these conflicts by allowing controlled vapor transmission. Through a microporous structure, they let air and moisture move at a calibrated rate—fast enough to maintain reaction balance, yet tight enough to block leaks and external contamination. This selective permeability is what keeps desiccant materials active, predictable, and safe throughout their service life.
At Kae Hwa, this principle defines every layer design. Our breathable films are engineered with specific WVTR (Water Vapor Transmission Rate) values tailored to different product chemistries, ensuring that each application—from moisture absorbers to heat-generating packs—operates precisely as intended.
Material Design and Functional Architecture
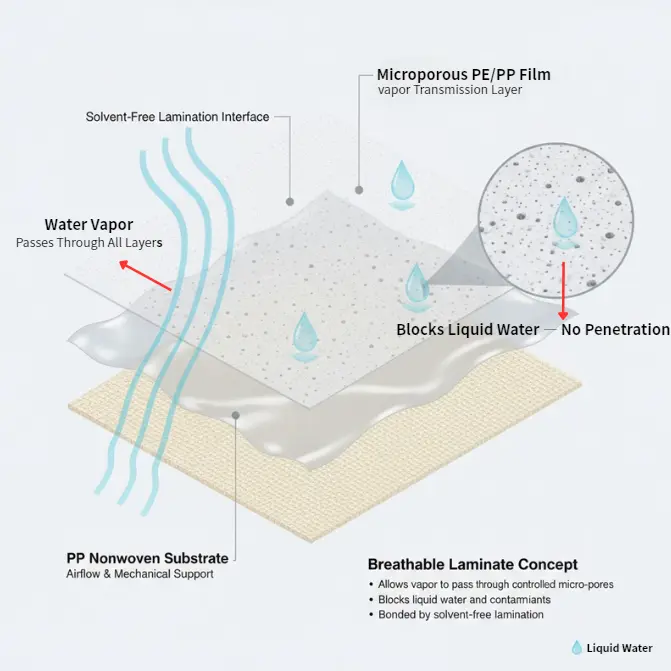
Building on this design principle, the effectiveness of each packaging film relies on the physical architecture that governs moisture diffusion and structural stability. Instead of a single polymer layer acting as a passive barrier, Kae Hwa develops composite laminates that coordinate vapor transmission, mechanical strength, and sealing performance across multiple layers.
The functional top layer operates as a selective gateway for vapor transmission. Microporous polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) films regulate diffusion through controlled pore geometry and distribution, enabling consistent vapor flow while maintaining resistance against liquid penetration and external contamination.
Beneath the film, the nonwoven carrier layer provides uniform airflow and tensile reinforcement. Its open-fiber matrix stabilizes the film during lamination and heat sealing, prevents localized condensation, and promotes uniform absorption within the active material. Once bonded under controlled temperature and pressure, these layers act as a unified membrane, maintaining WVTR stability under varying ambient humidity.
This engineered layer configuration allows Kae Hwa to fine-tune permeability, tensile strength, and seal performance for each packaging formulation—ensuring optimal function for moisture absorbers, deodorant sachets, and oxidation-based heat packs.
Functional Performance in Everyday Applications

The functional benefits of Kae Hwa’s breathable packaging materials derive directly from their engineered layer architecture. Each performance attribute—moisture regulation, gas exchange, mechanical durability—is governed by the balance between the microporous film and its nonwoven carrier. This coordination ensures that the packaging material performs not merely as a container, but as an active interface that supports product chemistry and long-term stability.
In hand warmers, the laminated film precisely controls the rate of oxygen ingress. This regulates the iron oxidation reaction that produces heat, maintaining a steady temperature curve instead of a rapid initial surge followed by decline. Even under fluctuating ambient humidity, the film maintains consistent gas permeability while preventing liquid intrusion or powder leakage.
For deodorant or odor-control packs, where activated charcoal or zeolite relies on surface adsorption, the film’s microstructure facilitates slow vapor diffusion without condensation. This allows odor molecules to be captured efficiently while keeping the adsorbent dry and active. The nonwoven substrate distributes air uniformly across the sachet surface, avoiding localized saturation and maintaining continuous deodorizing performance.
In desiccant sachets and moisture absorber packs, controlled vapor transmission is essential to prevent premature saturation. A WVTR precisely matched to the sorbent kinetics allows gradual water uptake over extended storage periods, protecting electronics, pharmaceuticals, and general packaged goods from humidity spikes.
Across these applications, Kae Hwa’s breathable film laminates deliver stable vapor diffusion and maintain reliable material strength throughout downstream converting processes such as cutting, laminating, or heat-applying by customers. The materials are designed to integrate smoothly with typical packaging workflows without causing issues during processing. Each property is evaluated and validated based on the environmental conditions the finished products are expected to encounter, ensuring consistent and dependable material performance.
Sustainability and Material Safety
Beyond functional performance, every Kae Hwa packaging material is developed under a design philosophy that emphasizes environmental responsibility and product safety. Material sustainability begins at the molecular level—through the selection of recyclable polymers and manufacturing processes that reduce emissions and waste.
The laminated structures used in Kae Hwa’s breathable films are composed primarily of polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), both widely recyclable thermoplastics recognized for their chemical stability and low environmental footprint. Kae Hwa’s production capability includes solvent-free lamination technology for combining breathable films with nonwoven substrates, reducing process emissions and material waste during manufacturing.
From a safety and compliance standpoint, these film–nonwoven laminates are validated through performance standards such as ASTM E96 for water vapor transmission rate and EN 20811 for hydrostatic resistance. They are widely applied in hygiene, protective, and specialty packaging, including desiccant solutions.
As global consumers increasingly seek environmentally friendly packaging options, desiccant wrappers and breathable films align with the industry’s commitment to reducing waste and environmental impact. By integrating these principles into every stage of material development, Kae Hwa ensures that sustainability is not an afterthought—but an intrinsic part of its breathable film technology.
Customization Options for Different Packaging Needs
Every moisture-control application demands a different balance between barrier protection and breathability. To address these varying requirements, Kae Hwa engineers design film–nonwoven laminates with adjustable parameters such as WVTR, film thickness, pore morphology, and bonding method. These variables determine how moisture and air interact within the package, ensuring the material performs in sync with each product’s functional chemistry.
For instance, desiccant pouches or absorber packs used in electronics often require low to medium WVTR values to prolong shelf life and avoid rapid saturation. In contrast, oxidation-based products such as hand warmers depend on higher gas permeability to sustain controlled oxygen inflow. Kae Hwa’s breathable films can be tuned through polymer selection—using microporous PE or PP membranes to achieve the required vapor transmission rate and diffusion control under various humidity conditions.
Lamination methods can also be customized. Depending on the converting process, films may be supplied as single-layer membranes, duplex laminates, or multi-layer composites with optional color, texture, or printable surface finishes. Roll width and basic weight can be adapted to automated packing lines for efficient integration into mass production.
By combining these customization options, Kae Hwa delivers tailored breathable packaging materials that match each customer’s operational environment—from small-format sachets to large industrial packs—without compromising durability, sealing quality, or breathability consistency.
Partner with Kae Hwa for Reliable Moisture Control Solutions
With decades of experience in breathable film and nonwoven integration, Kae Hwa delivers reliable materials for moisture-control packaging. Its in-house lamination and converting capabilities allow quick adaptation to different WVTR targets and package formats.
FAQ
Q1. How does breathable film improve moisture control compared to plastic bags?
A1. Microporous films let humidity escape at a controlled rate, avoiding condensation and premature saturation. Traditional plastic bags trap moisture, reducing the effectiveness of the desiccant over time.
Q2. What materials are commonly used for breathable desiccant film?
A2. Most breathable films are made from polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP). These thermoplastics are lightweight, recyclable, and suitable for lamination with nonwoven fabrics.
Q3. How is the water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) adjusted in desiccant packaging?
A3. WVTR can be modified by changing the film thickness, pore size, and lamination structure. A higher WVTR allows faster vapor release, while a lower WVTR helps maintain longer-term dryness.
Q4. What type of packaging benefits most from breathable films?
A4. Products such as desiccant sachets, moisture absorber bags, deodorant packs, and hand warmers use breathable films to manage humidity or oxygen flow during storage and activation.